ERPC Performs Major Upgrade and Restarts Large Solana RPC Node in Singapore to Meet Growing Low-Latency Demand Across Asia
ERPC Performs Major Upgrade and Restarts Large Solana RPC Node in Singapore to Meet Growing Low-Latency Demand Across Asia
ELSOUL LABO B.V. (headquartered in Amsterdam, Netherlands; CEO: Fumitake Kawasaki) and Validators DAO are pleased to announce that ERPC has performed a major upgrade of its large Solana RPC node (HTTP/WebSocket) in the Singapore (SGP) region at a data center on Solana’s primary network, and has resumed operations in this new configuration.
As a result, round-trip ping to Solana’s primary network layer has improved from more than 1ms to the 0.x ms range. For users accessing from Singapore, Vietnam, Hong Kong, Taiwan, China, and other parts of Asia, we have confirmed clear performance improvements.
Solana usage across Asia has been steadily increasing, and this upgrade is part of ERPC’s efforts to address both the growing demand and the need for faster, more stable infrastructure.
Why Singapore Is Important for Solana Use Cases
Singapore is one of Asia’s major international financial centers and a hub where many multinational companies and trading-related businesses are concentrated. It is also home to a large number of data centers and serves as a key landing point for submarine cables connecting countries across Asia. This results in low round-trip latency to major cities such as Shanghai, Taipei, Ho Chi Minh City, and Jakarta.
Within the Solana ecosystem, Singapore is one of the regions targeted by incentive pool staking programs, where initiatives to increase validator participation are actively underway. From both a network topology and staking distribution perspective, Singapore is a logical and important choice when designing infrastructure for Solana workloads.
By performing a major upgrade of ERPC’s large RPC node in Singapore on the primary network layer of Solana, we have created an environment that makes it easier for users and developers across Asia to access this critical part of the network.
Details of the Major Upgrade on Solana’s Primary Network Layer
In the previous configuration, the Singapore RPC node operated one network layer away from Solana’s primary network. This left room for additional hops and path variability. As a result, even though average latency was already low (around 1–2ms), there were situations where the timing of block and log retrieval showed noticeable variation.
With this upgrade, the large RPC node in Singapore has been rebuilt to operate on the same network layer where stake is heavily concentrated within the Solana network. Round-trip ping to the primary network has improved from more than 1ms to the 0.x ms range.
This change brings the following characteristics:
- Block and log retrieval timing is more stable on a slot-by-slot basis
- Latency variance caused by jitter on intermediate network paths is reduced
- More stable Shreds reception also contributes to more stable indexing
In addition to lowering average latency, Shreds — which are required for data synchronization — are delivered over UDP, meaning that fewer external network hops result in faster and more stable reception. With this upgrade, the Shreds delivery path has been minimized, making block and log retrieval more stable than before. This is one of the key improvements of this upgrade.
Growing Blockchain Demand in Asia and Existing Challenges
In recent years, interest in blockchain and Web3 has continued to rise across Asia. In countries and regions such as Japan, South Korea, China, Singapore, Taiwan, and Vietnam, there has been a noticeable increase in hackathons, community events, and other activities focused on Solana and other public blockchains. The number of developers working with these technologies is also expanding.
At the same time, it has long been difficult in Asia to secure access to high-speed and robust RPC infrastructure.
Examples of the structural challenges include:
- Developers often connect from local environments or cloud providers to RPC nodes located in distant regions, resulting in large network distances
- Issues may not be apparent during development, but tend to surface under real production load or during periods of high traffic
- Because network distance itself is a bottleneck, there is a hard limit to what can be improved solely through code optimization or better hardware
With the major upgrade and restart of the large RPC node in Singapore, ERPC aims to mitigate some of these bottlenecks at the network layer and provide an environment that better supports development and production workloads across Asia.
ERPC’s Design Policy: Operating Nodes Within Solana’s Primary Network
ERPC’s shared nodes operate within the same network as Solana’s primary network. In Solana, the number of leader slots assigned to a validator is proportional to its stake, and Shreds are propagated to validators in order of stake weight. Because of this, the network where the largest amount of stake is concentrated is also the layer that receives Shreds the earliest. ERPC defines this network as the “Solana primary network.”
By placing shared nodes in this layer, ERPC can access the latest data at the shortest possible distance without traversing the external internet.
This configuration allows blocks, logs, Shredstream, and gRPC data to be processed over the shortest paths, making them less susceptible to variability caused by network distance or path changes.
The major upgrade of the large RPC node in Singapore also follows this basic policy. By further reducing the distance to the primary network, ERPC aims to improve both the consistency and stability of processing.
Solana RPC Bundle Plan

ERPC offers the “Solana RPC Bundle” plan, which allows users to access multiple high-performance Solana data channels in a single package. The Bundle plan includes:
- Solana RPC (HTTP / WebSocket)
- Geyser gRPC (no filter restrictions)
- Shredstream gRPC
Many developers and projects start by using Geyser gRPC to consume real-time data, and later integrate Shredstream to move their detection and transaction submission closer to the leading edge. The Bundle plan is designed to support this step-by-step performance upgrade without requiring downtime or disruptive changes to existing production environments.
Positioning of Premium Ryzen VPS
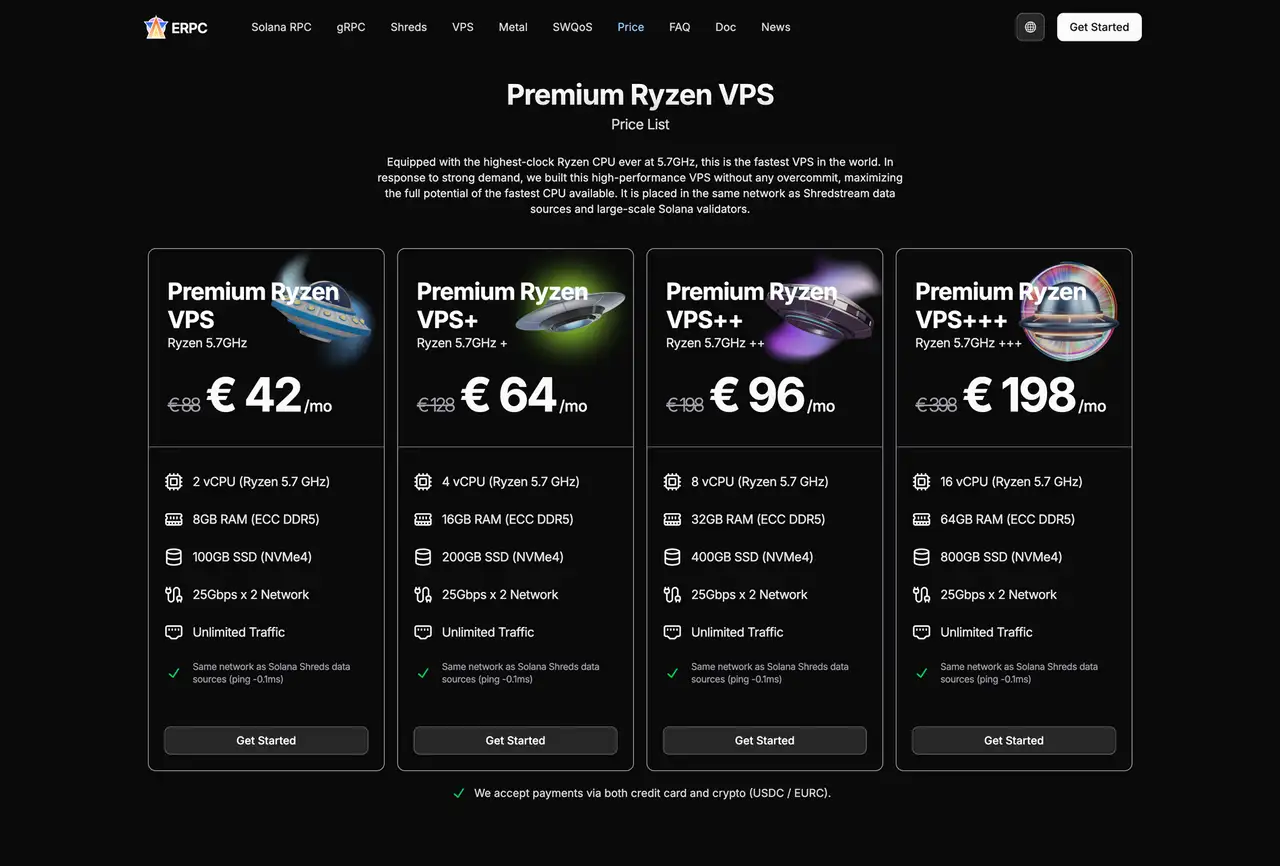
For many projects, deploying bare-metal servers in every region is not realistic. As a result, we often see architectures where some key locations (for example, Frankfurt) are optimized with bare-metal servers for maximum performance, while other regions are covered by Premium Ryzen VPS.
Premium Ryzen VPS offers configurations such as the following (example):
- 5.7GHz-class Ryzen CPUs (among the highest clock speeds available)
- ECC DDR5 memory
- NVMe4 storage
- 20–50Gbps dedicated network bandwidth
- A no-overcommitment, dedicated design
This makes Premium Ryzen VPS suitable for applications that do not require full bare-metal capacity, while still providing a high-performance environment operating inside the primary network at a realistic cost.
Availability and Contact
Bare-metal servers in the Singapore region are currently fully sold out and available only via a waitlist.
For advice on selecting the most appropriate configuration for your use case, as well as information on Bundle plans, Premium Ryzen VPS, and inventory or waitlist status in Singapore and other regions, please contact us through the Validators DAO official Discord.
Validators DAO Official Discord: https://discord.gg/C7ZQSrCkYR
Challenges Addressed by ERPC, SLV, and Validators DAO
- Transaction failures and latency variance in typical RPC environments
- Performance limits imposed by many infrastructure providers
- The significant impact of network distance on communication quality
- The difficulty smaller projects face in securing high-quality infrastructure
During the development of Epics DAO, a Solana-based NFT card game, we encountered these issues first-hand, particularly the challenge of obtaining high-performance development environments. In response, we built our own platform and operational expertise. ERPC and SLV are provided on top of that foundation.
We will continue to adapt our infrastructure to the structure and demand of the Solana network, working to improve developer experience and contribute to better user experiences for applications built on Solana.
- ERPC Website: https://erpc.global/
- SLV Website: https://slv.dev/
- elSOL Website: https://elsol.app/
- Epics DAO Website: https://epics.dev/
- Validators DAO Official Discord: https://discord.gg/C7ZQSrCkYR